In the summer, engineers always worry about overheating the motor. But everyone knows that measuring the degree of motor heating is to use "temperature rise" instead of "temperature." The test of temperature involved in the motor test is mainly the temperature rise test and the ambient temperature test. This paper mainly introduces the difference and relationship between the two.
First, the motor temperature rise test
The motor starts to run at normal temperature (the temperature of each part is the same as the ambient temperature), and the temperature rises continuously. When it rises above the ambient temperature, it continues to absorb heat and slowly heats up. On the other hand, it begins to radiate heat to the surroundings. When the motor is in the heat balance state and the temperature is no longer rising, the difference between the temperature of the motor and the ambient temperature is called the motor temperature rise. Both: temperature rise = motor temperature - ambient temperature, in K.
The maximum allowable temperature of the motor is the highest temperature that the winding can withstand. When used at this temperature for a long period of time, the physical, mechanical, chemical and electrical properties of the insulating material do not undergo significant malignant changes. If the temperature exceeds this temperature, the properties of the insulating material may change qualitatively or cause rapid aging. Therefore, the maximum allowable operating temperature of the insulating material is determined based on its economic useful life. The maximum allowable temperature of the motor is determined, and the temperature rise limit depends on the temperature of the cooling medium. In general, the cooling medium in the motor is air, and its temperature varies with region and season. In order to manufacture motors that can be applied throughout the country throughout the year, and to clarify uniform inspection standards.
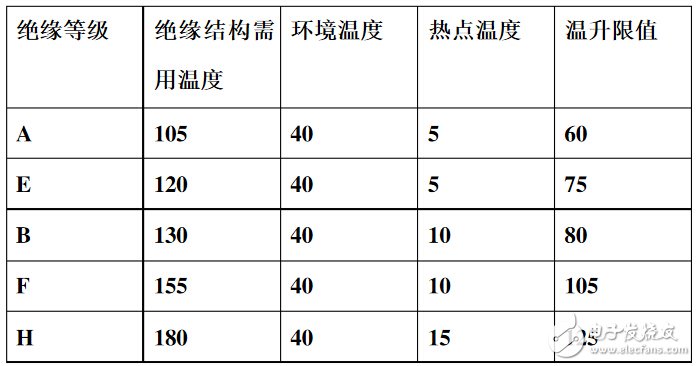
Figure 1 Motor insulation level comparison table
Although the temperature measurement of the motor winding and other parts has been adopted by many advanced technologies, it can be summarized into three basic methods: the electric resistance method, the thermometer method and the embedded thermometer method.
Resistance method: The resistance of the conductor increases with the increase of temperature. The relationship between resistance and temperature rise is as follows. The temperature rise measured by the resistance method is the average temperature rise of the winding, which is about 5 degrees Celsius lower than the hottest point of the winding. The measurement of the resistance can be measured by voltammetry or bridge method. After the power is turned off, the measured temperature rise is lower than the actual temperature at the moment of power-off.
Thermometer method: The temperature rise of the motor is directly measured by a thermometer. When the motor reaches the rated operating state, its temperature gradually rises to a certain stable value and no longer rises. At this time, the temperature of the motor can be measured with a thermometer. The temperature measured by this method is the local temperature of the measuring point.
Buried thermometers are used to embed thermocouples or RTD thermometers in the manufacturing process of the motor, which cannot be reached after the motor is manufactured. This method is mainly used to measure the temperature of the AC stator winding, core and structural parts. This method requires at least six thermometers to be embedded between the winding layers of the motor, distributed along the circumference, and placed on the hottest part of the winding as much as possible while ensuring safety, and avoiding the thermometer Contact with the cooling air, for the use of air-cooled motor is the highest temperature reading of the thermometer to determine whether the temperature rise of the winding is satisfactory.

Figure 2 Motor embedded thermometer
Second, the motor ambient temperature test
For some motors that actually operate in a high temperature environment, the actual ambient temperature should be simulated during the type test, and then the load test should be performed. For this type of test, the motor to be tested is usually covered with a thermostat and heated. Experiment with the actual ambient temperature.
Motor ambient temperature testing generally focuses on two directions:
1. Perform extreme environmental endurance tests for special high and low temperature motors. For example, high-temperature motor is made of high-temperature resistant insulating material, which can ensure the safe operation of the motor in high temperature environment, no aging, no burning, high-temperature motor application range, market prospects can be expected. Its motor performance is designed according to the characteristics of the fan pump type, which can save energy.
2. Measure the running state of the motor under constant temperature and eliminate the influence of temperature on the operating parameters of the motor.

Figure 3 Motor environment experiment box connection diagram
Third, the impact of environmental temperature changes on the temperature rise of the motor
The temperature rise measured during the winter of the same motor is low, and the temperature measured during the summer is increased. For a normal running motor, the temperature rise in the rated load is not related to the ambient temperature, but it is actually subject to the ambient temperature. And other factors affect it. When the ambient temperature drops, the temperature rise of the normal motor will decrease slightly. This is because the winding resistance r is lowered and the copper loss is reduced. For every 1 °C drop in temperature, r is reduced by about 0.4%.
Jiangmen soundrace electronics and technology co.,ltd. , https://www.soundracegroup.com