Currently, telecommunication operators mainly use PPPoE access control to develop broadband access services, and use Radius authentication to manage users. This method uses dynamic allocation of IP addresses to control the bandwidth of each user, which supports the development of broadband services. Due to the diversified development trend of broadband application services, especially the launch of the pilot work of triple play, streaming media services such as IPTV and smart device access application services are different from general web content push broadband services, and the PPPoE access method has been unable to meet Development requirements. The IPoE access control method does not require the installation of a client program and does not require the input of user names and passwords. It is a zero-configuration deployment and is very suitable for new network terminal equipment, such as IPTV set-top boxes, WLAN, handheld IP terminals, video surveillance, VoIP, etc. Terminal. In the context of triple play, IPoE is particularly meaningful in providing access control solutions for the development of large-scale IPTV services. Currently, mainstream access authentication control technologies mainly include PPPoE and IPoE.
PPPoE (PolntoPoilltProtocaloverEtherne) refers to carrying the PPP protocol on Ethernet, using Ethernet to form a large number of hosts into a network, accessing the Internet, and controlling each connected host. PPPoE is the encapsulation of PPP on Ethernet, which provides the ability to communicate point-to-point on an Ethernet broadcast link. The PPP protocol passes through three protocol negotiation stages: link control protocol LCP, authentication protocol (PAP, CHAP), and network control protocol NCP, which solves the problems of link establishment, maintenance, teardown, upper layer protocol negotiation, and authentication. After dialing, the user computer and the local access server (BRAS) negotiate the underlying link parameters in the LCP phase; in the authentication phase, the user name and password are sent to the access server for authentication. The access server can perform local authentication, which can be passed through the RadiSS protocol. The user name and password are sent to the AAA server for authentication. After the authentication is passed, in the NCP (IPCP) negotiation stage, the access server assigns network layer parameters (such as IP address, etc.) to the user computer. After the three PPP negotiation phases are successful, users can send and receive network packets, and all network layer packets sent and received by users are encapsulated in PPP packets. The identity verification function of the PPP protocol solves the problem of user security management on Ethernet well.
PPPoE authentication is widely used because of its standard and good interoperability, and its commercial use is mature; PPPoE authentication dial-up software is well compatible with mainstream PC operating systems, or has been built into the operating system; PPPoE passes a unique Session-ID It can well guarantee the security of users and is widely used in broadband access authentication.
PPPoE's authentication mechanism is relatively complex, and it handles the performance of the device. Memory resource requirements are high, and users need a waiting process for authentication. Because PPPoE ends in BRAS, there is a large number of point-to-point connections established by PPP between BRAS and the host, the switch passing through cannot recognize the PPPoE message format, and can only forward it, and cannot multicast the information such as VLAN. Replication, so that the multicast replication point can only be selected on the BRAS device. The limitations exposed by BRAS equipment cannot meet the rapid development of broadband multimedia services.
IPoE uses DHCPOPTION information to achieve zero-configuration deployment of service terminals. IPoE can realize authentication and automatic configuration by means of Yuansu user name and password, and can also implement authentication based on user name and password by DHCP + Web.
DHCP refers to the dynamic host configuration protocol. Through the DHCP client, the automatic discovery mechanism is used to try to establish communication with the DHCP server. DHCP provides IP configuration parameters to configure the IP layer on the user side. The DHCP protocol does not have the authentication function, but can cooperate with other technologies to achieve authentication, such as DHCP + Web mode, DHCP + client mode, and use DHCP + OPTION to extend authentication. These methods are collectively referred to as DHCP + authentication. Now the main discussion is the DHCP + OPTION extended field for authentication, also known as IPoE authentication. The OPTION fields used for DHCP extension are mainly OPTION60 (RFC2132) and OPTION82 (RFC3046). Among them, OPTION60 carries Vendor and Service Option information, which is the information carried when the user terminal initiates a DHCP request, and the network device only needs to transmit transparently. Its role is to identify the user terminal type, and then identify the user service type, the DHCP server can assign different business IP addresses accordingly. The OPTION82 information is inserted into the DHCP message sent by the terminal by the network device, which is mainly used to identify the access location of the user terminal, realize the precise binding of the user and the line, and ensure the security and authenticity of DHCP access. The information can be inserted by DHCPSnooPing or DHCPRelay equipment.
The user terminal device as an IPoE client generates a DHCP message, and the intermediate device inserts various DHCP options to perform user binding and service binding. Broadband Network Gatewny, such as BRAS or SR, is responsible for the translation of DHCP messages to Radius authentication messages. Perform authentication, authorization, and billing functions with Radius. After the authentication is passed, the functions such as the QoS per user returned by Radius and the list of access control are decentralized, and the traffic / duration passed through the device is charged. IPoE service control systems such as Radius can dynamically adjust the bandwidth and QoS attributes of each user, and provide multiple billing methods based on prepayment, traffic, and duration. Manage and control users, and provide differentiated services.
Based on the user's physical location (VLANyVCID) authentication and billing, there is no need to enter a user name and password when connecting to the network, which is very suitable for always-on applications and users who are unwilling to enter the user name and password.
DHCP + (option60 / Option82) extends the DHCP protocol and adds features such as security (protection against DoS attacks and address phishing), monitoring, and user identification. Combined with Radius to provide billing function, easy to operate.
· Flexible deployment of multicast, which can efficiently realize multicast replication, and move the multicast replication point down to the end of the network such as community switches and DSLAM. Reduce network pressure and save access network bandwidth.
Security measures for IPoE certification
IPoE authentication does not provide a unique point-to-point communication mechanism at the network level like PPPoE authentication. Operators should focus on security issues when deploying IPoE authentication. Devices at all levels of the network work together to enhance the security of the network. The specific security measures are as follows:
· Anti-spoofing
DHCP is a control method that separates data and authentication, and its security is not as good as PPPoE. To prevent users from statically configuring IP addresses or network theft, MAC + IP binding can be deployed on access devices or service routers. A node that enables DHCP Snooping or DHCP Relay generates a binding relationship between IP and MAC when it listens to a DHCP Offer message. Only IPoE frames that match the source MAC and IP can pass, otherwise it is discarded. In this way, only users who have been authenticated by DHCP can get network services. Terminals without authentication or statically configured IP addresses cannot be served. You can also identify and authenticate the user's line number based on OPTION82 information to ensure security.
· Limiting the number of user terminals The system limits the number of user terminals connected to each service access point.
· Anti-DOS attack
Bind the user's MAC address and line number in Radius. The MAC address and line number are queried in the Radius database, and the DHCP requester can be sent to the DHCP server after being authenticated by the Radius server to obtain the IP address. This method reduces the risk of attacking the DHCP server by sending a large number of DHCP requests and simulating requests with different MAC addresses.
Before users obtain IP addresses through authentication, set a limit on the number of DHCP data packets that can pass to reduce the pressure on Radius Server. If the number of Radius requests from the same DSLAM line number is controlled, for example, a maximum of 1 request is allowed within 1 s. If multiple requests appear consecutively, an attack is considered to occur and the Radius data packet is directly discarded. Rely on this mechanism to solve the risk of sending a large number of DHCP requests to the Radius server.
· Other safety measures
Isolation of direct forwarding ports between user ports is forbidden; business isolation is achieved through VLAN isolation.
2.3 Comparative analysis of PPPoE and IPoE
After introducing the IPoE system, IPoE can complete all the functions of the original PPPoE system, while also providing the following advantages:
(1) Terminal support
All devices that support the IP protocol are supported, without the need to install third-party dial-up software, and can widely support various handheld devices, mobile devices, video devices, etc.
(2) Message overhead
Since PPPoE packets introduce PPPoE headers (6Bytes) and PPP headers (2Bytes), a protocol overhead of 8 bytes is added to all user traffic. For high-bandwidth applications (8M HDTV, etc.), the processing power is not High terminal equipment is under great pressure.
(3) Multicast replication
Because PPPoE messages establish a point-to-point connection between the BRAS device and the user, the intermediate switch layer does not understand the PPPoE message format very well, and can only be forwarded, and cannot effectively replicate multicast information such as VLANs. Therefore, using PPPoE to carry out the multicast service, the multicast replication point can only be a BRAS device, while using IPoE, the multicast replication point can be moved down to the DSLAM, which reduces the pressure on the BRAS device on the one hand, and it is also extremely The earth saves network access layer bandwidth.
(4) User redundancy
The IPoE mode can control the number of connected users. For example, the Portal mode has strong value-added service capabilities.
According to the above discussion, IPoE authentication has obvious advantages in terms of terminal support, encapsulation overhead, and multicast support authentication efficiency. The disadvantage is that the user control is insufficient, and needs to be improved in user authentication / policy control / address allocation / session monitoring.
3 Business push control technology implementation
3.1 Analysis of single-edge and multi-edge access control
Due to the obvious advantages of IPoE in carrying new services such as IPTV, it may become the main authentication method in the future. PPPoE, as the current main authentication method for broadband services, will also exist for a long time. According to different business types, flexibly choose IPoE and PPPoE authentication methods. The same set of Rashan us systems can support two authentication methods. By deploying a multi-edge access architecture, achieving fine-grained control and QOS assurance for each user / service is the direction of business integration.
(1) Single edge access control
As shown in Figure 1, the single-edge service access mode means that the user's broadband Internet service and IPTV service share the same access control point BRAS. PC uses PPPoE to access BRAS. TV can use PPPoE or DHCP / private line to access BRAS. When using PPPoE, you can use different domain names or different VP / LVACN to distinguish whether the access comes from the set-top box or from the PC; when using DHCP, you can use the MAC address of the set-top box and DHCP Option60, or DHCP Option82 to control the pair The set-top box is assigned an address. For the NGN voice service carried by the broadband network, BRAS can be used as a PE to build an MPLS VPN.

Figure 1 Single edge access
(2) Multi-edge access control
As shown in Figure 2, the multiple (dual) edge access mode means that broadband Internet access services and IPTV services are provided by dedicated service access control points, respectively. The original BRAS is still used as the service control point for the broadband Internet access service; the SR is used as the control point for the IPTV service, and the DHCP / private line access method is used for the STB; the NGN voice service uses another SR as the control point, or shares the SR with the IPTV service. Different services are generally separated by the aggregation switch according to the VLANID and enter the corresponding service control equipment.
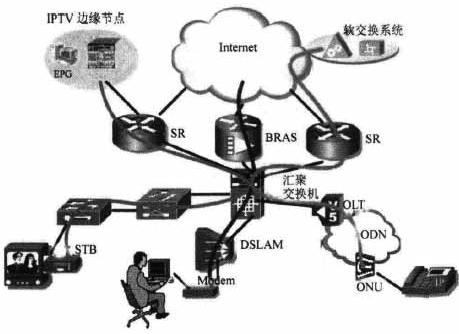
Figure 2 Multi-edge access
(3) Service access control scheme
If single-edge access is adopted, as the number of IPTV users increases, the BRAS load will increase, resulting in a strain on the port bandwidth. If BRAS doubles as PE, the equipment may be overwhelmed. In theory, the Internet service, IPTV service, and NGN voice service can share BRAS access, but the actual application needs to consider the bearing capacity of the device and the design positioning of the device.
If multiple (dual) edge access control methods are used, it is necessary to deploy different Layer 2 virtual channel PV (/ LVAC) for each service of each user in the Layer 2 access network from the terminal, which will increase the Layer 2 network Complexity. To reduce complexity, single-channel access can be used, and then the service awareness of the aggregation switch can be used to separate different services. This approach makes it difficult for different services to access control points, and to perform flow control and coordination between different services.
In the early days of network construction, BRAS can be used as an access gateway for IPTV services, but as the number of users grows, BRAS bearer pressure increases. Therefore, SR can be set up as an access control point for IPTV business services (see Table 1).
Table 1 Selection of access control methods
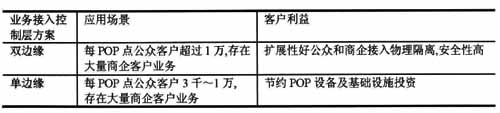
If the scale of POP users on the metropolitan area network is too large, it is recommended to use the dual-edge / multi-edge method, and some county-level POP points with small business volume and small business development potential use the single-edge method. Use one solution as much as possible within the same metropolitan area network. If the IPTV service is BRAS as the service control point, it is usually provided by PPPoE and Radius authentication. If SR is used as the service control point, it is usually provided by IPoE and DHCP authentication.
3.2 Broadband network service gateway
From the previous technical analysis, it can be seen that IPoE and PPPoE will coexist for a period of time to meet different business needs. No matter what authentication mechanism is adopted, a service access control gateway needs to be deployed to access users. Management of authentication, session and QOS strategies. Network edge service control equipment has evolved from devices that only support PPPoE (such as BRAS) to broadband network service gateways defined by the TR101 architecture (BNG supports both PPPoE and IPoE). The traditional BRAS is a device designed to support the PPPoE protocol and evolves into a BNG device by adding IPoE functions. Traditional service routers support high-bandwidth IPoE user control, and evolve into BNG equipment by adding PPPoE functions.
The access network is the bandwidth bottleneck of the metropolitan area network, and the QOS control mechanism of the residential Ethernet switch is weak. The H-QOS mechanism needs to be deployed on the gateway device to reduce the QOS performance requirements of the access network device and simplify QOS management. It is required that BNG can achieve up to three levels of scheduling to implement QoS policies for each user, service, and application, thereby achieving flexible bandwidth scheduling and service management.
3.3 IPoE deployment solution
IPoE is divided into non-Session level and Session level out of RAS centralized control of user sessions, authentication and address allocation) two ways. If the IPTV service is provided in a multi-edge manner, there is no need for session-level control, and a non-session-level method may be used; otherwise, the session-level method is used. Session-level IPoE is more suitable for the deployment of current and future services, realizing multi-service bearing and refined service operations.
(1) IPoE deployment based on BRAS IPoE deployment
· The existing network can support the large-capacity BRAS of IPoE, and can be deployed through software upgrades and hardware board expansion to achieve a single-edge architecture for integrated service carrying.
· The existing network cannot support IPoE's small-capacity BRAS, and the status quo should be maintained to carry PPPoE. At the same time, a large-capacity BRAS device is newly deployed at its location to carry IPoE services, that is, a dual-edge architecture of PPoE + IPoE. After the small-capacity BRAS gradually withdraws from the network, the large-capacity BRAS realizes a single-edge architecture for integrated service carrying.
(2) IPoE deployment is based on BRAS, SR distributed IPoE deployment
Combined with the current deployment status of existing equipment, SR can also be deployed to specifically carry video services such as IPTV, so that BRAS and SR can divertly carry services and share the load.
(3) Deployment of DHCPServer system
In the IPTV service, it is recommended that the IPTV service address be managed in a unified manner, and the DHCP Serve system (including the DHCPServer, authentication server, and database) is deployed centrally to allocate P addresses to IPTV terminals. The service router (SR) enables the DHCP Relay function, and Not a built-in DHCP server. The DHCP Server system is the core of IPoE service network authentication and is responsible for user authentication and address allocation. The centralized deployment of DHCP Server facilitates the deployment of unified address allocation strategies. These address allocation strategies, combined with other network control and management strategies, can provide differentiated services, resulting in a series of value-added products, such as VIP customers' address pools and network QoS The combination can guarantee the IPTV service experience of VIP customers.
1.HI tech integrated design, put Solar Panel,led light,controller and battery all in one box,without any cable, very easy for shipment , installation and maintenance
2.Eco friendly with Solar power supply
3.this design is to put high efficiency monocrystalline silicon solar panel,LED lamps,long life Lithum battery and controller all in one box
4.Different power of the light,meet the different requirements used in the road,house or other sites
5.From 15W up to 100W for LED lamps
Integrated Solar Street Light,Integrated Solar Led Street Light,All In One Solar Led Street Light,Integrated Solar Light
Yangzhou Beyond Solar Energy Co.,Ltd. , https://www.ckbsolar.com